TO BE ATTACKED BY THE ENEMY IS A GOOD THING
On May 26, 1939, at a time when the Communist Party of China was under heightened attack by
reactionaries, Mao Zedong wrote an influential three page article, “To Be Attacked by the
Enemy is Not a Bad Thing but a Good Thing”. This article was later included in the
Selected Readings from the Works of Mao Tsetung (Peking [Beijing]: 1971), and was also
included in Volume 6 of the Selected Works of Mao Tsetung published in India. It is
available online at:
http://www.marxists.org/reference/archive/mao/selected-works/volume-6/mswv6_32.htm
The basic theme of that fine article is
summed up in this paragraph:
“I hold that it is bad as far as we are concerned if a person, a
political party, an army or a school is not attacked by the enemy, for in that case it
would definitely mean that we have sunk to the level of the enemy. It is good if we are
attacked by the enemy, since it proves that we have drawn a clear line of demarcation
between the enemy and ourselves. It is still better if the enemy attacks us wildly and
paints us as utterly black and without a single virtue; it demonstrates that we have
not only drawn a clear line of demarcation between the enemy and ourselves but achieved
a great deal in our work.” —Mao Zedong, SR, p. 160.
TOILETS
“Percentage of people worldwide who lack access to a toilet or an outhouse: 41%”
—“Harper’s Index”, Harper’s Magazine, January 2008, p. 15.
[The next time you hear some pro-capitalist
asshole talk about how great the world supposedly is today because of capitalism, remember this
little fact, along with all the rest of the constant misery that exists for billions upon
billions of people in the world today, the starvation, the wage slavery, the endless imperialist
wars, and on and on. —Ed.]
TOKYO FIREBOMBING [By the U.S. in World War II]
The purposeful murder of vast numbers of civilians in a major fire storm in Tokyo, Japan, caused
by incendiary bombs dropped all around the city especially in residential areas, by the United
States beginning in the early hours of March 10, 1945. This was a major war crime, though no
punishment for it was ever administered or even contemplated. The damage to the city and the
number of civilian deaths was comparable to that caused by the American nuclear weapons dropped
on Hiroshima and Nagasaki five months later.
“Seventy-five years ago, less than 10 miles from where he now lives alone
in a low-lying neighborhood known for its moderate rents, Saotome (pronounced SAH-oh-toe-meh)
survived the brutally effective American firebombing of Tokyo. Over the course of nearly
three hours, an attack by the United States Army Air Forces killed as many as 100,000
people—more than some estimates of the number killed the day of the nuclear bombing of
Hiroshima. But while the Japanese public—and the world—rightly remember Hiroshima as a
living symbol of the horrors of nuclear war, the Tokyo firebombing is generally regarded as
a footnote in any accounting of the war in Japan.” —Motoko Rich, “This Survivor of the
Firebombing of Tokyo Won’t Let Us Forget”, New York Times, September 6, 2020.
[When imperialist powers go to war,
whether against small “Third World” countries or against each other, they don’t care how
many innocent people they murder; in fact, the more the better, they usually think. —Ed.]
“Over several hours, U.S. Army Air Forces warplanes destroyed the
shitamachi, or the low-lying section of Tokyo, and killed an estimated 100,000
Japanese citizens in a firestorm. The United States Strategic Bombing Survey later wrote
that ‘probably more persons lost their lives by fire at Tokyo in a six-hour period than at
any time in the history of man.’ The devastating results motivated military leaders to
continue incendiary bombing raids on Japan’s other cities—both large and small—in hopes of
forcing the Japanese to surrender. Before the war’s end, firebombs dropped by B-29s killed
hundreds of thousands of Japanese citizens in more than 60 cities before nuclear bombs
leveled Hiroshima and Nagasaki.” —John Ismay, “‘We Hated What We Were Doing’: Memories
From the Airmen”, New York Times, September 6, 2020.
TOLERANCE
Tolerance is a somewhat ambiguous concept, with both positive and negative aspects or interpretations.
Merriam-Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary, 10th ed., defines the relevant sense of the word ‘tolerance’
this way: “sympathy or indulgence for beliefs or practices differing from or conflicting with one’s own; [or]
the act of allowing something.” But there are many things we should and do “tolerate” in the views and ideas
of others—in the sense of allowing them (and not attempting to forcibly suppress them), but with regard
to which we still have no “sympathy” whatsoever, and for which we have political and social obligations to
seriously struggle against ideologically. This is true with respect to wrong or reactionary ideas among the
masses, and even at times, among our comrades. (And they have this same obligation with respect to wrong or
lingering bourgeois ideas they see in us!) So in a limited sense we tolerate wrong or bad ideas among the
masses (including within the revolutionary Party); and in more complete sense we do not tolerate them
without appropriate struggle against those bad ideas! To fail to do so would be to violate Mao’s injunction
to “combat liberalism”.
“Tolerance is the virtue of the man without convictions.” —G. K. Chesterton.
[Chesterton, though a religious reactionary himself, has here pointed to the general error of those
who use the excuse of “tolerance” to avoid struggle against wrong and harmful ideas. —Ed.]
“TOO BIG TO FAIL”
Capitalism is an unstable system in many respects, and specifically competitive capitalism
is unstable in that there are powerful forces which tend to transform it in the direction
of monopoly, as Marx pointed out long ago. When severe economic crises develop, however,
this creates additional major problems. It is no longer a question of a number of fairly
inconsequential small companies going bankrupt, but now a question of some extremely large
banks and other corporations failing. Some of these large corporations are now so important
for the economy that their failure would lead to such drastic repercussions that the
capitalist class in general has been forced to declare them “too big to fail”. In other
words, it is forced to use its control of the state to bail
out these giant banks and other corporations which it deems “too big to fail”.
In the Panic of 2008-9, which is part of
the overall still-developing profound world capitalist economic crisis, the U.S. government
has already spent literally trillions of dollars in both temporary and permanent bailouts
of banks and corporations which it considered “too big to fail”. This has become a major
feature of the crisis and will remain so from now on.
“By dividing the whole circulation [of bank notes] into a greater
number of parts, the failure of any one [banking] company, an accident which, in the
course of things, must sometimes happen, becomes of less consequence to the public.”
—Adam Smith, The Wealth of Nations, Book II, Ch. II, (Modern Library,
1937), p. 313.
[What Adam Smith did not understand,
however, is that the growth of monopoly is in the interests of the most important and
influential capitalists, who therefore also normally control the bourgeois state. Thus
even if there are nominal laws against monopoly, there will eventually come to be giant
monopolistic (or at least oligopolistic) corporations whose failure would indeed be
tremendously disruptive to the entire capitalist economy. Therefore it is inevitable that
banks and corporations “too big to fail” arise, and that the bourgeois state will then
bail them out and prop them up when they get into financial difficulty. It is today a
petty-bourgeois pipe dream to think that corporations can be kept small and inconsequential
enough so that their individual failures really do not matter.]
TOO FAR AHEAD OF THE PEOPLE
Getting too far out ahead of the people is one of the serious problems that can arise for a
political party, even a genuinely revolutionary party, when it tries to implement social
changes—even really good changes which are actually in the interests of the people—but when the
people themselves are not yet ready for those changes, and either still oppose them, or
at least are not very enthusiastic about the idea. The problem is that this is an arrogant and
undemocratic way of leading or ruling, and a way which causes that party to lose the respect and
support of the masses.
Unlike with bourgeois political parties, the way
that truly Maoist parties attempt to make changes in society is first through education,
and then through leadership of the masses in action—but only when the masses are themselves ready
to act. Mao expressed all this beautifully as follows:
“To link oneself with the masses, one must act in accordance with the
needs and wishes of the masses. All work done for the masses must start from their needs
and not from the desire of any individual, however well-intentioned. It often happens that
objectively the masses need a certain change, but subjectively they are not yet conscious
of the need, not yet willing or determined to make the change. In such cases, we should
wait patiently. We should not make the change until, through our work, most of the masses
have become conscious of the need and are willing and determined to carry it out. Otherwise
we shall isolate ourselves from the masses. Unless they are conscious and willing, any
kind of work that requires their participation will turn out to be a mere formality and
will fail.... There are two principles here: one is the actual needs of the masses rather
than what we fancy they need, and the other is the wishes of the masses, who must make up
their own minds instead of our making up their minds for them.” —Mao, Quotations
From Chairman Mao Tse-tung (Peking: 1966), pp. 124-5; originally in “The United Front
in Cultural Work” (October 30, 1944), SW3:236-7.
“Shen Hsien-e was the beautiful young woman whose father had forced her
into a prearranged marriage while she was still below the legal age limit.... But when I
left Long Bow [village] in August, 1948, county leaders had not settled the question of
a divorce for Hsien-e. They had sent her husband, Wang Wen-te, off to a special training
class for Communists who could not ‘pass the gate’ (i.e., win the approval of the
populace as Communists and cadres) while Hsien-e remained at her father’s home, where
she had been living ever since she made contact with the Women’s Association.... In spite
of Hsien-e’s earnest demand for a legal solution to this problem [i.e., for a divorce],
the district officials put off any decision in her favor. No divorce had ever ended a
marriage in Long Bow. Most people still opposed divorce, any divorce, on any grounds, on
principle.... The revolutionary officials had to support justice, they had to support
women’s rights, but at the same time they could not get too far ahead of the people as a
whole. Where no consensus prevailed in the community in favor of divorce, it behooved
them to move slowly, do more educating, and wait until public opinion caught up with the
requirements of the time. That was the ‘mass line’.
“Such was one argument for moving slowly.
A second argument had to do with the ultraleft tendency that distorted the whole Party
rectification campaign in 1948.... In the summer of 1948, a period when the Party set out
to correct the worst abuses brought about by this situation, no one wanted to rush into
granting a divorce for Hsien-e.... [Her husband] Wang Wen-te categorically opposed the
divorce... No one wanted to add to the long list of excesses that had been imposed on
village cadres since rectification began. This was, after all, a contradiction among the
people and not one between the people and their enemies.
“In the end, in spite of the fact that
Wang Wen-te did confront his mistakes at the cadre school, did return to Long Bow as a
Communist in good standing, did ‘pass the gate’ there and did resume his post as head of
the village police, the authorities granted a divorce to Hsien-e. They granted it because,
even though Wen-te opposed it to the end, his wife had a legal right to it. [Under the
new revolutionary regime. —Ed.] They did not consider the divorce a punishment, but only
a logical consequence of the fact that Wen-te had mistreated and alienated his unwilling
bride. Thus this story had a happy ending.”
—William Hinton, Shenfan, (NY:
Random House/Vintage, 1984), pp.22-24.
TOTAL AGREEMENT
It is difficult to believe that there is ever any such thing as absolutely total agreement between
two different human beings, on every single idea and on every imaginable issue. Of course a lacky or
sycophant might feign complete and total agreement with their boss or leader or guru, or even be
so trained to be intellectually submissive that they might feel compelled to adopt the entire
viewpoint of the “dominant mind” as soon as they learn what that is. And one of the two might not have
thought about some particular issue much at all, while the other has studied and considered the issue in
depth. But to really, truly, sincerely agree about absolutely everything, the two would have to both be
equally knowledgeable and equally ignorant, and at least one of them would in essence have no independent
mind or brain of their own.
And yet, quite strangely, many political groups or parties
seem to believe that one of their most important tasks is to try to achieve absolute and total unity on
all political and ideological matters, and that the existence of any continuing disagreement or difference
of opinion whatsoever within their ranks is a dangerous and intolerable thing, which simply has to be
immediately dealt with! Many political cults and sects, like
religious cults, expel or excommunicate anyone who insists on holding to some idea or point of view which
differs from the group’s established doctrine. Others only do that after the failure of endless rounds of
browbeating and harassment.
Since the early days of Marxism, as created by Marx and
Engels, genuine Marxist (or today Marxist-Leninist-Maoist) groups and parties, try to have a different
approach entirely. We have always tried to defend democracy within our organizations, including the right
to form, hold to, and defend individual opinions. Of course there needs to be some common sense with regard
to this principle. An individual who does not understand and agree with at least most of the basic ideas
of a Marxist revolutionary party should obviously not be a candidate to join such a party. But on the other
hand, insistence on complete and total agreement on every single point cannot be reasonably required either!
For one thing, some correct principles of MLM can only be fully and deeply grasped after considerable
study and social practice. And for another thing, our organizations and our overall revolutionary movement
can still be very effective even if some disagreements and differences of opinion do remain among us.
And here is a point that non-dialecticians may not be able
to grasp: Differences of ideas and opinions within our own ranks can sometimes actually prove to be a
very positive thing! The fact is that sometimes each one of us is wrong about some particular point,
and once in a while even our whole revolutionary organization or party will be quite wrong about something.
In that case we will need another idea, another approach, another method, or another opinion. And, fortunately
in any worthwhile real-world revolutionary organization there will be other opinions within it, and/or among
the masses of people it is connected with. And in this situation we even have an extremely valuable tool to
seek out these very important alternative ideas and approaches: namely, the mass
line, or what Mao called the leadership method of “from the masses, to the masses”.
Of course the mass line is mostly a tool of use in leading
mass struggles. So, then, what about differences over theoretical matters, such as how to understand certain
points in Marxist political economy, or dialectical materialism? Shouldn’t we more or less insist on doctrinal
purity in those theoretical areas at least? Of course we want to come to mostly agree on matters of theory
as well as on the tactics and strategy of the revolutionary struggle. But it is downright unscientific to
assume that our existing revolutionary theory is already 100% correct, even in supposedly esoteric areas such
as philosophy! In other words, it is quite possible that even in such theoretical areas, at least some of our
existing ideas might be wrong. And if they are in fact wrong, it is a good thing that a few people, even
within our own ranks, are exploring other possibilities. Sure, much of the time these “original thinkers”
will in fact turn out to wrong too, and even sometimes ridiculously wrong-headed! But once in a while they
might have a valuable correction which enables us to improve our revolutionary theory and our revolutionary
work.
Why do we try so hard to implement the principles of
democratic centralism in our MLM revolutionary parties? It is so
that we can collectively act as though every single member completely agrees on what is correct and
precisely what should be done at the present time, even though we know full well that there are still
many differences of understanding and opinion among us. Democratic centralism is the tool we use to both act
in the most effective, unified way, and at the same time to encourage and preserve the serious individual
thinking of every communist about how to advance the revolution. Of course every revolutionary comrade will
have their own ideas and will struggle with others to explain and promote those ideas because they believe
them to be correct. However, if we are smart enough to understand that good ideas arise in different heads at
different times, then we should actually also be smart enough to oppose the cultist point of view that everyone
should be hounded until they totally agree about everything. If, after some effort, we are unable to convince
a revolutionary comrade that they are wrong about some point or principle, then we would allow the matter to be
set aside for the time being, or to be put on the back burner for awhile. After all, we can be sure that
differences of opinion will come up again of their own accord; they always do eventually. —S.H.
[03/19/23]
See also:
GOING AGAINST THE TIDE,
THINKING JUST ALIKE
“When two guys agree, one of them is unnecessary.” —Line from the movie I
Cover the Waterfront (1933).
“TOTAL FACTOR PRODUCTIVITY”
See: PRODUCTIVITY—“Total
Factor”
TOTAL FERTILITY RATE
 The number of children that would be born to a woman if she were to live to the end of her
child-bearing years and bear children in accordance with the current age-specific
fertility rates. Although the TFR is one of the better measures of fertility in different
countries at use at the present time, it tends to overstate actual fertility levels during
periods when fertility rates are rapidly declining (as is the case at present in most parts
of the world).
The number of children that would be born to a woman if she were to live to the end of her
child-bearing years and bear children in accordance with the current age-specific
fertility rates. Although the TFR is one of the better measures of fertility in different
countries at use at the present time, it tends to overstate actual fertility levels during
periods when fertility rates are rapidly declining (as is the case at present in most parts
of the world).
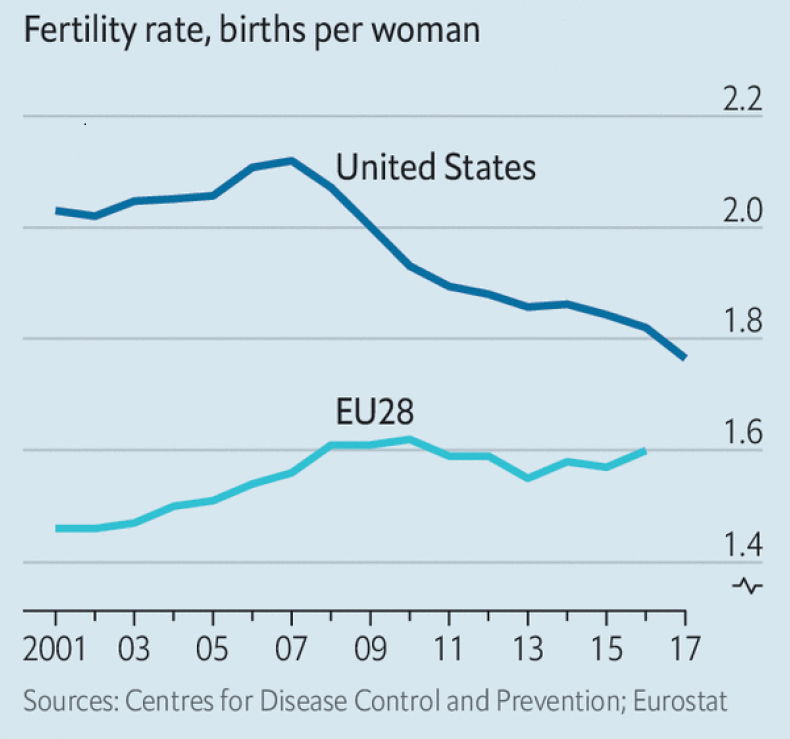
The Total Fertility Rates have been declining
in almost every country as the people of the world have been more and more squeezed by the
world capitalist overproduction crisis that has been developing since the early 1970s. It is
more and more economically infeasible for people to have children! For various reasons the
U.S. TFR has remained higher than that of most advanced capitalist countries, including Europe
and Japan. But the special circumstances that have kept the U.S. TFR rate higher are now less
and less effective, and the TFR in the U.S. is now quickly falling towards European levels.
(See graph at the right.) Although there are also other social factors at work, just as in
the Great Depression of the 1930s a low and/or falling birth rate is still a solid indicator
of the worsening economic condition of the people.
“Soon after the great recession hit America, in 2007, the birth rate
began to fall. Many people lost their jobs or their homes, which hardly put them in a
procreative mood. But in the past few years the economy has bounced back [according to
largely phony official statistics! —Ed.]—and births continue to drop. American’s total
fertility rate, which can be thought of as the number of children the average woman will
bear, has fallen from 2.12 to 1.77. It is now almost exactly the same as England’s rate,
and well below that of France.” —“The Birth Rate: Baby Bust”, The Economist,
Nov. 24, 2018, p. 23.
Dictionary Home Page and Letter Index
MASSLINE.ORG Home Page
 It has long been known that the CIA and other branches of the U.S.
government routinely use torture in their interrogations of people. This was finally even
officially admitted in a Senate report on CIA torture in 2014. The Obama administration then
piously condemned the use of torture, while at the same time continuing torture and U.S.
imperialist terrorism around the world through the use of drone
attacks and in many other ways. (This hypocrisy is ridiculed in the cartoon at the
right.)
It has long been known that the CIA and other branches of the U.S.
government routinely use torture in their interrogations of people. This was finally even
officially admitted in a Senate report on CIA torture in 2014. The Obama administration then
piously condemned the use of torture, while at the same time continuing torture and U.S.
imperialist terrorism around the world through the use of drone
attacks and in many other ways. (This hypocrisy is ridiculed in the cartoon at the
right.) The number of children that would be born to a woman if she were to live to the end of her
child-bearing years and bear children in accordance with the current age-specific
fertility rates. Although the TFR is one of the better measures of fertility in different
countries at use at the present time, it tends to overstate actual fertility levels during
periods when fertility rates are rapidly declining (as is the case at present in most parts
of the world).
The number of children that would be born to a woman if she were to live to the end of her
child-bearing years and bear children in accordance with the current age-specific
fertility rates. Although the TFR is one of the better measures of fertility in different
countries at use at the present time, it tends to overstate actual fertility levels during
periods when fertility rates are rapidly declining (as is the case at present in most parts
of the world).